Aim of the Center for Educational Innovations and Smart Education (hereinafter - "CEI Smart"):
- to improve the quality of training young specialists through the introduction of new forms and methods of education.
Objectives of CEI Smart:
- improving the quality of specialists’ training through toughening the qualification requirements;
- activization of innovative activities of bachelor, master and doctoral students and teachers;
- formation of new scientific approaches to the educational and professional content of the University courses (implementation of practice-oriented bachelor degree programs);
- testing of pedagogical theories and best practices in the field of modern higher and secondary professional education;
- introduction of innovative and proven technologies, methods and techniques of teaching in the educational activities of the University.
- creating a Smart learning model that implies creating an intelligent, high-tech, human-friendly learning environment using modern information and organizational systems;
- participation in the organization and creation of educational programs for new specialties;
- participation in the formation of an industry-wide system of qualifications in the field of ICT;
- participation in the development of professional standards in the ICT sector;
- implementation of the certification system for the qualification of specialists in the field of ICT;
- ensuring interaction with industry and regional authorities for the development of technical and vocational education and training of ICT personnel.
One of the objectives of the Center for educational innovations and Smart education is to introduce Smart learning technologies into the educational process of IITU. To this end, the CEI Smart has organized seminars for the IITU teaching staff, developed methodological guidelines, and compiled a schedule for the presentation of educational materials to the master program students.
SMART education is an educational paradigm that involves adaptive implementation of the educational process, which is possible through the use of SMART information technologies. The implementation of the SMART education paradigm aims at shaping the process of learning and education for the acquisition of knowledge, skills, abilities and competencies necessary for flexible and adaptive interaction with the changing social, economic and technological environment. SMART education should provide an opportunity to take advantage of the global information society to meet the national educational needs and interests.
The main principles of SMART education include the following:
- Use of up-to-date information in the educational program for solving educational problems: the speed and volume of information flow in education and any professional activity is rapidly increasing, the existing educational materials need to be supplemented with real-time information to prepare students for solving current practical problems.
- Organization of the students’ independent educational, research, and project activities. This principle is dominant in preparing students for creative search for solutions to problems, independent information processing and research activities.
- Implementation of the educational process in a distributed learning environment. The educational environment should not be limited to the educational institution premises or to the confines of the educational system. The learning process should be ongoing.
- Flexible educational paths, individualization of education. The diversity of educational activities requires the provision of wide opportunities for students to study educational programs and courses, use educational tools in accordance with their health, material and social conditions.
Smart Education is a concept that involves a comprehensive modernization of all educational processes, as well as methods and technologies used in such processes. The concept of Smart in the educational context entails the emergence of technologies such as "smart" board, "smart" screens, Internet access from anywhere. Each of these technologies allows you to build a new process of content development, delivery and updating. Learning becomes possible not only in the classroom, but also at home and in any public places, such as museums, cafes, and so on. The main element linking the educational process to the everchanging environment is active educational content used to create unified repositories that allow to remove the time and space frames. As practice shows, the economy increasingly requires specialists knowledgeable in related industries, such as Bioinformatics, IT Genetics, Agro-Informatics, etc. So training IT specialists for such related fields is the call of the time.
The main directions of CEI Smart work:
Direction 1.
It is the concept of Smart Education that allows you to build the educational process in a new way. In the 2018/2019 academic year, IITU admitted students to the bachelor degree program in the specialty "Computer Science and organization of digitalization of education". All disciplines related to ICT within the work plan of this specialty are conducted by IITU, and pedagogical disciplines – under an agreement – by the Abay Kazakh National Pedagogical University (KazNPU). Their organization involves not only the IITU faculty, but also requires use of its laboratories and practical base, library.
Direction 2.
In the 2019/2020 academic year, work has begun on creating educational programs in Bioinformatics. Together with the Institute of Human and Animal Physiology, we are working on joint training of specialists in Bioinformatics at the bachelor's and master's levels. The biology-related disciplines will be conducted on the basis of the Institute with the involvement of doctors of science working for it. Master students will be able to choose dissertation topics related to real-life projects and, if necessary, get a part-time job in the respective field. The educational process is based on the concept of Smart Education. A Memorandum has already been signed between the two organizations and preparatory work is underway to implement the Bioinformatics specialty.
Direction 3.
The next project that is already being developed at the preparatory stage is Digital Law.
The Internet has become a major platform for creating, managing and developing large-scale business projects. Modern legislation does not yet fully regulate this new area with an eye to the international experience and current international legislation. In cyberspace, both specific offenses, such as violation of intellectual property rights (copyright, patent rights, secret production rights), and "ordinary crimes" are committed – fraud, extortion, illegal business, etc. At the same time, large companies must create a reliable protection of the IT systems that store confidential data, so as to enable such systems to resist cyber attacks.
As such, there is no separate branch of IT law at the moment. Lawyers who choose this direction have to be knowledgeable in several areas of law simultaneously: contract law, intellectual property law, regulation of personal data protection, storage and transfer of information, as well as its transfer in the electronic form. Many firms are already starting to create IT-legal departments or hire IT-lawyers. Among the bar associations, there are also those that provide services exclusively on cyber security issues, and large universities form faculties for training specialists in cyber law. In the era of technology, a lawyer specializing in the IT sphere has a wide range of opportunities. There is almost no competition among such specialists because of their shortage, and their experience and knowledge are priceless.
The absence of a system of training specialists in the field of digital law in the Republic of Kazakhstan is fraught with legal vulnerability of Kazakhstani firms and organizations not only in the external, but also in the internal market. The latter circumstance is clearly confirmed by the gradual but constant displacement of Kazakh law firms from the field of legal services provision to large Kazakh corporate businesses, which are ousted by almost exclusively foreign law firms. And what is most deplorable about this trend is the absolute openness, honesty and fairness of such displacement occurring due to technical, technological and conceptual superiority of western law firms in solving the international business issues.
The project aims: To improve the quality of training specialists in the field of ICT and digital law, create a single market for educational services, and introduce dual-diploma education.
Vision: Availability of competitive and mobile staff for Kazakhstan and the EEU.
Project participants: International Information Technology University (IITU), Abay Kazakh National Pedagogical University (KazNPU).
The project results are expected to provide:
- Creation and implementation of dual-diploma educational programs;
- Development of blended and mobile learning;
- Introduction of progressive teaching methods;
- Creation of a flexible educational environment;
- Launching a WEB portal for online learning;
- Open environment for sharing knowledge and experience;
- Creation of massive open educational content (MPEC);
- Development and implementation of Smart Education methodology and hardware-software;
- Working out curricula on the basis of advanced learning;
- Involvement of the best foreign practices in training specialists in digital law;
- Raising the quality of educational services and the competitiveness of specialists of the new formation;
- Delivery of advanced training courses in the field of digital law for specialists already working in various sectors of the economy of Kazakhstan.
Educational trajectory:
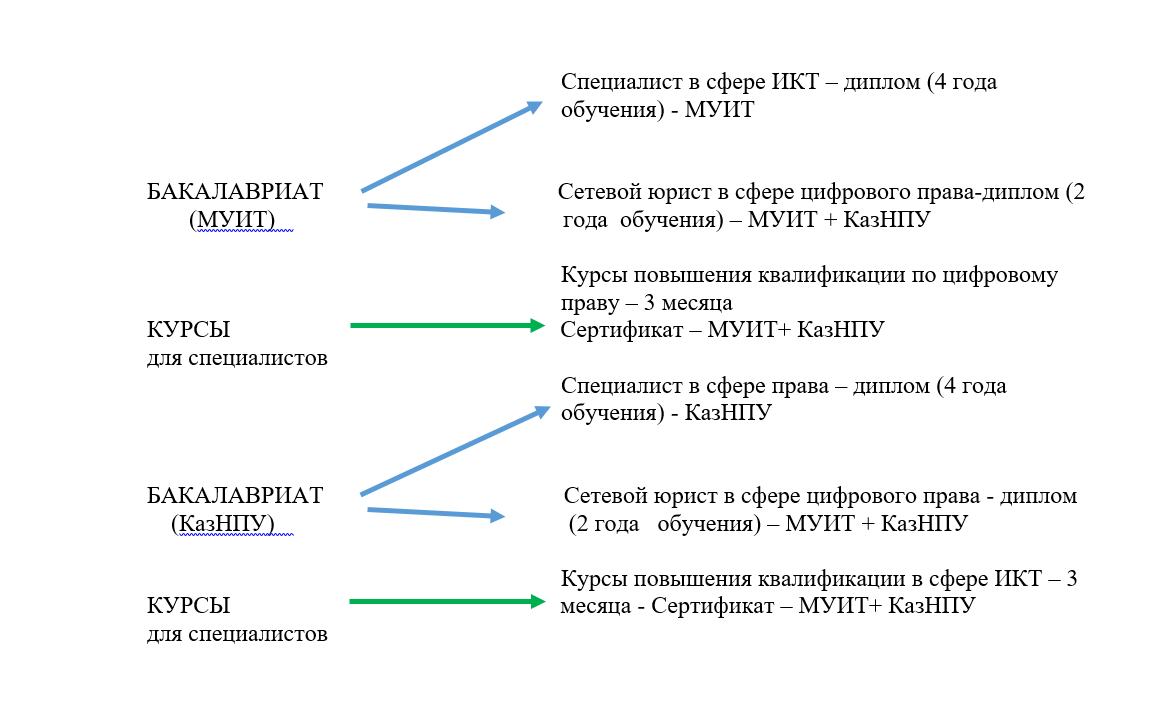
Project timeline:
Start of the project - 01. 12.2019;
Preparatory stage - until 01.03. 2020;
Start of the project implementation for bachelor's degree – 2020/2021 academic year.
Start of the project implementation for advanced training courses - 01.10.2020.
Direction 4.
Implementation of full-time online education in IITU
The structure of the distance learning format
Development of a distance learning format includes technological, content and organizational components.
- The technological component is based on the material and technical base: hardware (computers, etc.), software, technical support, software maintenance, system and content updates (upgrades).
- The content component is a structured educational content, which provides invariant components of a certain type of e-learning resources (ELR): DL courses, e-textbooks, specialized sites, portals, and their methodological support.
- The organizational component provides the organization and conduct of the educational process using various DL models.
These components make it possible to create a unified information and educational space that includes the educational process, its information support and management, as well as the use of modern pedagogical technologies that meet the requirements of the new educational paradigm.
Distance learning can be implemented only if the role of all participants in the educational process is correctly distributed and they work together. Undoubtedly, the technological component should be implemented by the IT support Department.
The preparation of the content part should be assigned to the Center for Educational Innovations and Smart Education with the active support of the university departments. The organizational component should be supervised by the Dean's office and the Department of postgraduate education, the Department of educational-methodological and academic work (Fig.1).
It is not foreseen at the initial stage to create new educational courses for bachelor and master students, but only to adjust and translate them into the electronic form in accordance with the DL requirements.
Within DL the main costs are required at the start-up stage of the project, and then they practically do not increase with an increasing number of students. In the first half of the 2019/2020 academic year it is planned to reduce the classroom load to 536 hours and to use the vacated classrooms more efficiently for the educational purposes.
Full-time online education is a cost-effective business. Depending on the size of the project, the payback period lasts on average from 1 (for small projects) to 2 years. Thus, this is one of the most profitable business segments at the moment.
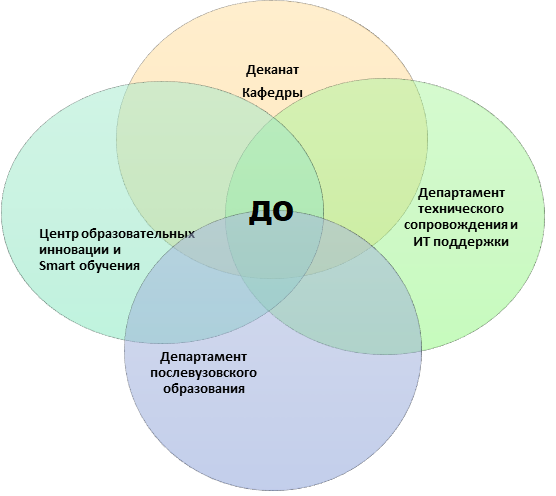
Figure 1 - Participation of IITU departments in the implementation of DL
The main system for implementing full-time online education for bachelor and master students is shown in Figure 2. In this case, only a part of the load is transferred to the online mode. The lecture and, if possible, practical classes are conducted in the webinar mode. Laboratory classes and part of practical classes are conducted in a full-time mode. As a rule, students are connected to the teacher's computer according to the schedule, the lecture lasts for 25-30 minutes, and the remaining time is used for interactive communication. The "blended learning" method of teaching is used, i.e. students should come to the lecture already prepared for the topic of the lesson, having familiarized themselves with the respective lecture on the University website.
The BigBlueButton program - an open source software for conducting web conferences - is used for the conduct of webinars. The system is designed primarily for distance learning. The name BigBlueButton comes from the original concept that starting a web conference should be as simple as possible, like pressing a metaphorical big blue button.
BigBlueButton supports multiple audio tracks and video sharing, the ability to display presentations, Microsoft Office and OpenOffice documents, images, and PDF documents. Advanced whiteboard features are also supported – such as pointing, zooming, drawing, and desktop access.
Students’ feedback in a web conference is managed via public and private chat rooms. VoIP is integrated on the base of FreeSWITCH. In addition, the user can log in to the conference either as a viewer or as a moderator. As a viewer, the user can join a voice conference, use a webcam, raise a hand (ask for a word), and communicate with other people.
ТУПы, РУПы –SACs, WCs
ЭОР – ELR
Обьявления - Announcements
МООС- MPEC
Кафедры- Departments
Тесты - Tests
Лекция - Lecture
Самостоятельные задания - Independent tasks
Консультация - Consultation
Преподаватель - Teacher
Деканат - Dean's office
Личный кабинет - Personal account
Сайт МУИТ - The IITU website
Магистры, студенты - Masters, students
Тьютор - Tutor
Очное обучение – Full-time education
Экзамен - Exam
Завершение курса – Course completion
Очно-сетевое обучение - Full-time online education
Учебный график – Academic schedule
ЭУМКД - EUMKD
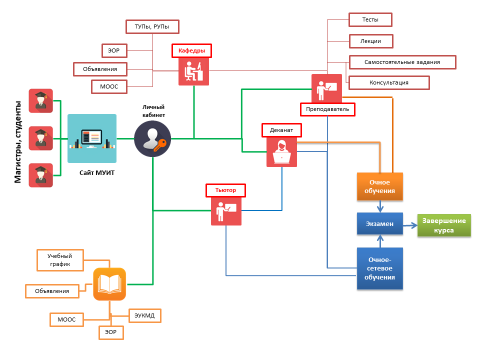
Figure 2- Full-time online education system for students and masters
As a moderator, the teacher has the ability to disable / enable the microphone of any student, remove any student from the web conference, and give the floor to any student (make any user the host). The presenter can upload presentations, documents, and use the whiteboard.
The next stage of the DL implementation (its expansion and improvement of the quality of the distance learning process) will require additional specialized equipment.
The essential advantage of SMART Education is the individual learning trajectory and its interactivity, which have become possible only with the help of innovative information and communication technologies.
